The world stands on the brink of a significant cocoa supply crisis, with repercussions that ripple through markets, economies, and the very fabric of the chocolate industry. A sequence of poor harvests in key West African cocoa-producing regions has set the stage for a third consecutive year of supply shortages, unveiling a series of challenges and concerns for stakeholders across the value chain.
The Root of the Turmoil: West Africa’s Dwindling Harvests
Central to the unfolding situation is the alarmingly poor crop yields from West Africa, a pivotal area for global cocoa production. This downturn in productivity has led to a supply deficit that threatens the stability and sustainability of the cocoa market. The impacts are far-reaching, affecting everyone from farmers to final consumers, and raise serious questions about future sourcing strategies and the viability of current agricultural practices.

The Double-Edged Sword of Financial Markets
Compounding the physical scarcity of cocoa beans are the dynamics within the financial markets. Some traders, in anticipation of future price movements, have engaged in selling futures contracts as a hedge against their physical holdings. This speculative activity necessitates substantial cash reserves to cover margin calls, especially in a market trending upwards. Such conditions can force traders to liquidate positions prematurely, inadvertently fueling further price increases.
A Surge in Prices: The New Norm?
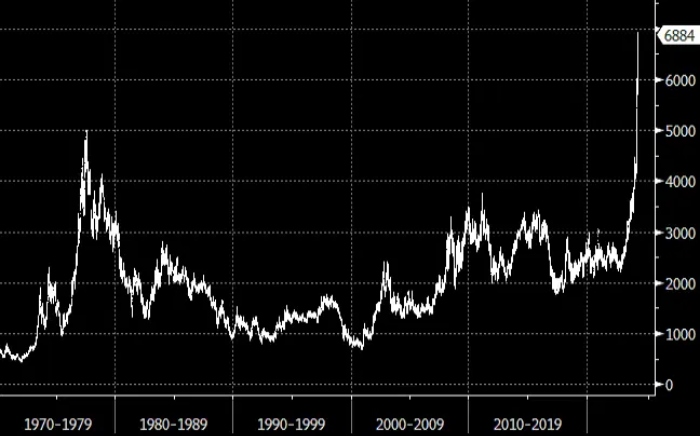
The price of cocoa has witnessed unprecedented surges, reaching heights that were previously unimaginable. For instance, futures prices soared by as much as 4.5% to $10,080 per ton in New York, signaling a shift into what many analysts consider overbought territory. Despite this, the upward trajectory of cocoa prices shows little sign of abatement, challenging conventional wisdom about market corrections and the role of speculative trading in price determination.
Analyzing the Price Phenomenon
Experts like Paul Joules from Rabobank have voiced concerns over the justification of these soaring prices. The market’s resilience in bouncing back from dips suggests strong buying pressure from commercial entities, hinting at underlying supply anxieties rather than mere speculative fervor. This scenario has led to speculation about potential profit-taking moments and the sustainability of the rally.